Seperti apa yang dikutip dari Wikipedia bahwa Jamur dalam bahasa Indonesia sehari-hari mencakup beberapa hal yang agak berkaitan. Arti pertama adalah semua anggota kerajaan Fungi dan beberapa organisme yang pernah dianggap berkaitan, seperti jamur lendir dan "jamur belah" (Bacteria). Arti kedua berkaitan dengan sanitasi dan menjadi sinonim bagi kapang. Arti terakhir, yang akan dibahas dalam artikel ini, adalah tubuh buah yang lunak atau tebal dari sekelompok anggota Fungi (terutama Basidiomycetes) yang biasanya muncul dari permukaan tanah atau substrat tumbuhnya. Pengertian terakhir ini berkaitan dengan nilai ekonomi jamur sebagai bahan pangan, sumber racun, atau bahan pengobatan. Bentuk umum jamur biasanya adalah seperti payung, walaupun ada juga yang tampak seperti piringan.
Beberapa jamur aman dimakan manusia bahkan beberapa dianggap berkhasiat obat, seperti jamur merang (Volvariela volvacea), jamur tiram (Pleurotus), jamur kuping (Auricularia polytricha), jamur kancing atau champignon (Agaricus campestris), dan jamur shiitake (Lentinus edulis). Jamur yang beracun contohnya adalah Amanita muscaria, dan jamur yang dikenal sebagai "destroying angel".
Ciri-Ciri Umum Jamur
Jamur merupakan kelompok organisme eukariotik yang membentuk dunia jamur atau regnum fungi. Jamur pada umumnya multiseluler (bersel banyak). Ciri-ciri jamur berbeda dengan organisme lainnya dalam hal cara makan, struktur tubuh, pertumbuhan, dan reproduksinya.
1. Struktur Tubuh
Struktur tubuh jamur tergantung pada jenisnya. Ada jamur yang satu sel, misalnyo khamir, ada pula
jamur yang multiseluler membentuk tubuh buah besar yang ukurannya mencapai satu meter,
contohnyojamur kayu. Tubuh jamur tersusun dari komponen dasar yang disebut hifa. Hifa
membentuk jaringan yang disebut miselium. Miselium menyusun jalinan-jalinan semu menjadi tubuh
buah.
Hifa adalah struktur menyerupai benang yang tersusun dari dinding berbentuk pipa. Dinding ini
menyelubungi membran plasma dan sitoplasma hifa. Sitoplasmanya mengandung organel eukariotik.
Kebanyakan hifa dibatasi oleh dinding melintang atau septa. Septa mempunyai pori besar yang
cukup untuk dilewati ribosom, mitokondria, dan kadangkala inti sel yang mengalir dari sel ke sel.
Akan tetapi, adapula hifa yang tidak bersepta atau hifa senositik.
Struktur hifa senositik dihasilkan oleh pembelahan inti sel berkali-kali yang tidak diikuti dengan
pembelahan sitoplasma.
Hifa pada jamur yang bersifat parasit biasanya mengalami modifikasi menjadi haustoria yang
merupakan organ penyerap makanan dari substrat; haustoria dapat menembus jaringan substrat.
Struktur tubuh jamur tergantung pada jenisnya. Ada jamur yang satu sel, misalnyo khamir, ada pula
jamur yang multiseluler membentuk tubuh buah besar yang ukurannya mencapai satu meter,
contohnyojamur kayu. Tubuh jamur tersusun dari komponen dasar yang disebut hifa. Hifa
membentuk jaringan yang disebut miselium. Miselium menyusun jalinan-jalinan semu menjadi tubuh
buah.
Hifa adalah struktur menyerupai benang yang tersusun dari dinding berbentuk pipa. Dinding ini
menyelubungi membran plasma dan sitoplasma hifa. Sitoplasmanya mengandung organel eukariotik.
Kebanyakan hifa dibatasi oleh dinding melintang atau septa. Septa mempunyai pori besar yang
cukup untuk dilewati ribosom, mitokondria, dan kadangkala inti sel yang mengalir dari sel ke sel.
Akan tetapi, adapula hifa yang tidak bersepta atau hifa senositik.
Struktur hifa senositik dihasilkan oleh pembelahan inti sel berkali-kali yang tidak diikuti dengan
pembelahan sitoplasma.
Hifa pada jamur yang bersifat parasit biasanya mengalami modifikasi menjadi haustoria yang
merupakan organ penyerap makanan dari substrat; haustoria dapat menembus jaringan substrat.
2. Cara Makan dan Habitat Jamur
Semua jenis jamur bersifat heterotrof. Namun, berbeda dengan organisme lainnya, jamur tidak memangsa dan mencernakan makanan. Clntuk memperoleh makanan, jamur menyerap zat organik dari lingkungan melalui hifa dan miseliumnya, kemudian menyimpannya dalam bentuk glikogen. Oleh karena jamur merupakan konsumen maka jamur bergantung pada substrat yang menyediakan karbohidrat, protein, vitamin, dan senyawa kimia lainnya. Semua zat itu diperoleh dari lingkungannya. Sebagai makhluk heterotrof, jamur dapat bersifat parasit obligat, parasit fakultatif, atau saprofit.
Parasit obligat
merupakan sifat jamur yang hanya dapat hidup pada inangnya. Sedangkan di luar inangnya tidak dapat hidup. Misalnya, Pneumonia carinii (khamir yang menginfeksi paru-paru penderita AIDS).
Parasit fakultatif
adalah jamur yang bersifat parasit jika mendapatkan inang yang sesuai, tetapi bersifat saprofit jika tidak mendapatkan inang yang cocok.
Saprofit
merupakan jamur pelapuk dan pengubah susunan zat organik yang mati. Jamur saprofit menyerap makanannya dari organisme yang telah mati seperti kayu tumbang dan buah jatuh. Sebagian besar jamur saprofit mengeluar-kan enzim hidrolase pada substrat makanan untuk mendekomposisi molekul kompleks menjadi molekul sederhana sehingga mudah diserap oleh hifa. Selain itu, hifa dapat juga langsung menyerap bahanbahan organik dalam bentuk sederhana yang dikeluarkan oleh inangnya.
Cara hidup jamur lainnya adalah melakukan simbiosis mutualisme. Jamur yang hidup bersimbiosis, selain menyerap makanan dari organisme lain juga menghasilkan zat tertentu yang bermanfaat bagi simbionnya. Simbiosis mutualisme jamur dengan tanaman dapat dilihat pada mikoriza, yaitu jamur yang hidup di akar tanaman kacang-kacangan atau pada liken.
Jamur berhabitat pada bermacam-macam lingkungan dan berasosiasi dengan banyak organisme. Meskipun kebanyakan hidup di darat, beberapa jamur ada yang hidup di air dan berasosiasi dengan organisme air. Jamur yang hidup di air biasanya bersifat parasit atau saprofit, dan kebanyakan dari kelas Oomycetes.
3. Perrtumbuhan dan Reproduksi
3. Perrtumbuhan dan Reproduksi
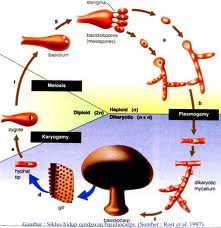
Reproduksi jamur dapat secara seksual (generatif) dan aseksual (vegetatif). Secara aseksual, jamur menghasilkan spora. Spora jamur berbeda-beda bentuk dan ukurannya dan biasanya uniseluler, tetapi adapula yang multiseluler. Apabila kondisi habitat sesuai, jamur memperbanyak diri dengan memproduksi sejumlah besar spora aseksual. Spora aseksual dapat terbawa air atau angin. Bila mendapatkan tempat yang cocok, maka spora akan berkecambah dan tumbuh menjadi jamur dewasa.
Reproduksi secara seksual pada jamur melalui kontak gametangium dan konjugasi. Kontak gametangium mengakibatkan terjadinya singami, yaitu persatuan sel dari dua individu. Singami terjadi dalam dua tahap, tahap pertama adalah plasmogami (peleburan sitoplasma) dan tahap kedua adalah kariogami (peleburan inti). Setelah plasmogami terjadi, inti sel dari masing-masing induk bersatu tetapi tidak melebur dan membentuk dikarion. Pasangan inti dalam sel dikarion atau miselium akan membelah dalam waktu beberapa bulan hingga beberapa tahun. Akhimya inti sel melebur membentuk sel diploid yang segera melakukan pembelahan meiosis.
4. Peranan Jamur
Peranan jamur dalam kehidupan manusia sangat banyak, baik peran yang merugikan maupun yang menguntungkan. Jamur yang menguntungkan meliputi berbagai jenis antara lain sebagai berikut.
a. Volvariella volvacea (jamur merang) berguna sebagai bahan pangan berprotein tinggi.
b. Rhizopus dan Mucor berguna dalam industri bahan makanan, yaitu dalam pembuatan tempe dan oncom.
c. Khamir Saccharomyces berguna sebagai fermentor dalam industri keju, roti, dan bir.
d. Penicillium notatum berguna sebagai penghasil antibiotik.
e. Higroporus dan Lycoperdon perlatum berguna sebagai dekomposer.
5. Di samping peranan yang menguntungkan, beberapa jamur juga mempunyai peranan yang merugikan, antara lain sebagai berikut.
a. Phytium sebagai hama bibit tanaman yang menyebabkan penyakit rebah semai.
b. Phythophthora inf'estan menyebabkan penyakit pada daun tanaman kentang.
c. Saprolegnia sebagai parasit pada tubuh organisme air.
d. Albugo merupakan parasit pada tanaman pertanian.
e. Pneumonia carinii menyebabkan penyakit pneumonia pada paru-paru manusia.
f. Candida sp. penyebab keputihan dan sariawan pada manusia.
Peranan Jamur Terhadap Pertumbuhan Tanaman.
Jamur berperan penting dalam pertumbuhan tanaman sebagai pengurai tanah dan kemudian menyediakan nutrisi penting bagi tanaman dari proses fermentasi dalam pengomposan. Selain itu Berkaitan dengan cara hidup jamur yang bersimbiosis mutualisme yang mana jamur menyerap makanan dari organisme lain dan juga menghasilkan zat tertentu yang dapat bermanfaat bagi peningkatan pertumbuhan tanamah. Simbiosis mutualisme jamur dengan tanaman dapat dilihat pada mikoriza (Rhizopogon sp.), yaitu jamur yang hidup di akar tanaman kacang-kacangan atau pada liken, dan yang menginfeksi berbagai akar tanaman hingga area penyerapan akar tanaman menjadi lebih luas.
Seperti dikutip dari faktailmiah.com bahwa Penelitian baru oleh para ilmuwan di Universitas Sheffield telah berhasil menjelaskan bagaimana tanaman pertama di bumi mulai memenuhi daratan lebih dari 470 juta tahun yang lalu dengan menjalin kemitraan dengan jamur tanah. Penelitian yang diterbitkan di Nature Communications, telah memberikan bukti penting yang hilang, yang menunjukkan bahwa kelompok tanaman purba bekerja sama dengan jamur tanah untuk ‘menghijaukan’ bumi pada era Paleozoikum awal, hampir setengah miliar tahun yang lalu.
Penelitian, yang juga melibatkan para ahli dari Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Imperial College London dan Universitas Sydney, telah memberikan wawasan baru ke dalam pemahaman kita tentang perkembangan perilaku dinamis tanaman dan jamur darat di bumi.
Para ilmuwan telah lama menduga bahwa jamur tanah menjalin hubungan saling menguntungkan dengan tanaman darat awal untuk berperan penting dalam membantu kolonialisasi awal pada lingkungan darat. Namun, hingga saat ini belum ada bukti yang menunjukkan bagaimana tanaman darat purba paling awal, dari era Paleozoikum awal (lebih dari 470 juta tahun yang lalu), mungkin telah bekerja sama dengan jamur untuk saling menguntungkan.
Tim peneliti mempelajari tanaman thalloid liverwort, jenis yang merupakan anggota dari kelompok tanaman darat paling purba yang masih ada dan masih menyimpan banyak fitur asli nenek moyangnya. Mereka menggunakan ruang pertumbuhan lingkungan terkontrol untuk mensimulasikan atmosfir kaya CO2, mirip dengan era Paleozoikum di mana tanaman tersebut berasal. Lingkungan ini secara signifikan memperkuat manfaat dari jamur bagi pertumbuhan tanaman serta awal jalinan hubungan antara tanaman dan mitra jamurnya.
Tim peneliti menemukan bahwa ketika thalloid liverwort dijajah oleh jamur, maka itu secara signifikan meningkatkan penyerapan karbon fotosintesis, pertumbuhan dan reproduksi aseksual, faktor yang berdampak menguntungkan pada kebugaran tanaman. Tanaman bertumbuh dan berkembang biak lebih baik bila dijajah oleh jamur simbiosis karena jamur tanah memberikan nutrisi penting. Sebagai gantinya, jamur juga memperoleh manfaat dengan menerima karbon dari tanaman. Penelitian ini menemukan bahwa setiap tanaman mendukung jamur yang memiliki area seluas 1-2 kali dari lapangan tenis.
Profesor David Beerling, dari Departemen Ilmu Hewan dan Tanaman di Universitas Sheffield, mengatakan, “Dengan mempelajari tanaman purba ini kita membuka sebuah jendela pada masa lalu untuk menyelidiki bagaimana tanaman darat awal berevolusi. Hasil kami mendukung gagasan bahwa ‘penghijauan’ bumi dipromosikan oleh simbiosis antara tanaman dan jamur. Hal ini menunjukkan bahwa tanaman tidak akan bertahan di daratan tanpa bekerja sama dengan jamur – hal ini telah lama dicurigai, tetapi sampai sekarang tidak terselidiki. Hal ini mengharuskan kita berpikir lagi tentang peran penting kerjasama di antara organisme yang mendorong perubahan mendasar dalam ekologi di planet kita.”
Martin Bidartondo dari Laboratorium Jodrell di Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, mengatakan, “Jamur ada di setiap jenis habitat di seluruh dunia dan sangat penting bagi banyak tanaman untuk bertumbuh. Hal ini menarik bahwa kita sekarang mulai menemukan jamur berasosiasi dengan tanaman ‘lebih rendah’, dan masih banyak lagi yang harus terus diselidiki.”
KNOW YOUR MUSHROOMS AND ITS EFFECT ON PLANT
Like what is quoted from Wikipedia that the fungus in the Indonesian language daily covering some things somewhat related. The first meaning is that all members of the kingdom Fungi and some who never thought to be related organisms, such as slime molds and "fission fungi" (Bacteria). The second meaning relates to sanitation and became a synonym for mold. Last meaning, which will be discussed in this article, is the body of the fruit is soft or thick of a group of fungi (mainly basidiomycetes) which usually arise from the surface of the soil or growth substrate. Understanding the past is related to the economic value of fungi as food, source of poison, or the treatment material. A common form of fungus usually is like an umbrella, although there also seemed like the dish.
Some mushrooms safe to eat humans and even some medications are considered nutritious, such as mushroom (Volvariela volvacea), oyster mushrooms (Pleurotus), ear mushroom (Auricularia polytricha), button mushroom or champignon (Agaricus campestris), and shiitake mushrooms (Lentinus edulis). A poisonous mushroom is Amanita muscaria for example, and fungi, known as the "destroying angel".
General Characteristics of Fungi
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that make up the world of mushrooms or fungi Regnum. Fungi are generally multicellular (many celled). The characteristics of different fungi with other organisms in terms of diet, body structure, growth, and reproduction.
1. Body Structure
Mushroom body structure depending on its type. There are single cell fungi, yeasts misalnyo, there are multicellular fungi that form large fruiting bodies that reach one meter in size, contohnyojamur wood. Mushroom body is composed of basic components, called hyphae. Hyphae form a network called mycelium. Interwoven mycelium develop pseudo-braided into fruiting bodies.
Hyphae are thread-like structures composed of tubular wall. This wall surrounds the plasma membrane and cytoplasm of hyphae. Cytoplasm containing eukaryotic organelles. Most hyphae is limited by transverse walls or septa. Septa have pores large enough to pass ribosomes, mitochondria, and sometimes the cell nucleus that flows from cell to cell. However, that does not bersepta adapula hyphae or hyphae senositik. Structure senositik hyphae produced by the cell nucleus division many times that is not followed by cytoplasmic division.
Hyphae of the parasitic fungus usually undergo modification into haustoria which is the organ of food absorbent substrate; haustoria to penetrate the substrate network.
2. How to Eat and Fungi Habitat
All types of fungi are heterotrophic. However, unlike other organisms, fungi are not prey and digest food. Clntuk obtain food, fungi absorb organic substances from the environment through the hyphae and miseliumnya, then save it in the form of glycogen. Because the fungus is a consumer then the mushroom depends on the substrate that provides carbohydrates, protein, vitamins, and other chemical compounds. All substances were obtained from the environment. As being heterotrophic, obligate parasitic fungi can, facultative parasites, or saprophyte. Obligate parasites is a fungus that only nature can live in its host. Meanwhile, outside of their host can not live. For example, Pneumocystis carinii (yeast that infects the lungs of AIDS patients). Facultative parasite is a parasitic fungus that if you get a suitable host, but is saprophyte if not get a suitable host.
Saprophyte
is a modifier composition rot fungi and dead organic matter. Saprophyte mushrooms absorb food from dead organisms such as fallen logs and fallen fruit. Most of the fungal saprophyte issued a hidrolase enzymes in the food substrate to decompose complex molecules into simpler molecules that are easily absorbed by the hyphae. In addition, the hyphae can also directly absorb organic bahanbahan in a simple form issued by the host.
is a modifier composition rot fungi and dead organic matter. Saprophyte mushrooms absorb food from dead organisms such as fallen logs and fallen fruit. Most of the fungal saprophyte issued a hidrolase enzymes in the food substrate to decompose complex molecules into simpler molecules that are easily absorbed by the hyphae. In addition, the hyphae can also directly absorb organic bahanbahan in a simple form issued by the host.
Another way of life is to do a symbiotic fungus mutualism. Symbiotic fungi that live, in addition to absorb food from other organisms also produce certain substances that are beneficial to simbionnya. Fungus mutualism symbiosis with mycorrhizal plants can be seen in, ie fungi that live on the roots of legumes or on Liken.
Fungi berhabitat on a variety of environments and associated with many organisms. Although most live on land, there are some fungi that live in water and in association with aquatic organisms. Fungi that live in water usually parasitic or saprophyte, and most of the class Oomycetes.
3. Growth and Reproduction
Sexual reproduction of fungi can be (generative) and asexual (vegetative). Asexually, fungi produce spores. Fungal spores of different shapes and sizes and usually unicellular, but those that multicellular. If suitable habitat conditions, the fungus multiplies by producing large amounts of asexual spores. Asexual spores can be carried by water or wind. When you find a suitable place, then the spores will germinate and grow into mature mushrooms.
Sexual reproduction in fungi through contact gametangium and conjugation. Contact gametangium singami cause, namely the union of two individual cells. Singami occurs in two stages, first stage is plasmogami (fusion of cytoplasm) and the second stage is kariogami (melting the core). After plasmogami occurs, the cell nucleus from each parent come together but not fused and formed dikarion. Couples in the cell nucleus will split dikarion or mycelium within a few months to several years. Eventually the cell nucleus fuse to form diploid cell that immediately meiotic division.
4. Role of Fungi
The role of fungi in human life very much, both the role of adverse or beneficial. Beneficial fungi include various types are as follows.
a. Volvariella volvacea (edible mushroom) is useful as a high protein food.
b. Rhizopus and Mucor useful in the food industry, namely in the manufacture of tempeh and oncom.
c. Yeast Saccharomyces useful as the fermenter in industrial cheese, bread, and beer.
c. Yeast Saccharomyces useful as the fermenter in industrial cheese, bread, and beer.
d. Penicillium notatum is useful as a producer of antibiotics.
e. Lycoperdon perlatum Higroporus and useful as a decomposer.
5. In addition to the beneficial role, some mushrooms also have a detrimental role, among others, as follows.
a. Phytium as a pest plant seeds that cause disease fall seeding.
b. Phythophthora inf'estan cause disease on leaves of potato plants.
c. Saprolegnia as parasites on the body of water organisms.
d. Albugo is a parasite on agricultural crops.
e. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia cause disease in human lung.
f. Candida sp. cause of vaginal discharge and sores in humans.
Role of Fungi on Growth of Plants.
Fungi play an important role in plant growth soil decomposers and then provide essential nutrients for plants from the fermentation process in composting. Also Regarding the symbiotic way of life mushroom fungus mutualism which absorb food from other organisms and also produce certain substances that can be useful for improving growth tanamah. Mutualism symbiotic fungi with plants can be seen in the mycorrhizal (Rhizopogon sp.), Ie fungi that live on the roots of legumes or on Liken, and that infects a variety of root crops to plant root absorption area becomes more widespread.
As quoted from faktailmiah.com that new research by scientists at the University of Sheffield has successfully explained how the first plants on earth began to fill the mainland more than 470 million years ago by establishing partnerships with soil fungi. The study, published in Nature Communications, has provided important evidence is missing, which suggests that an ancient group of plants in cooperation with soil fungi to 'greening' of the earth in the early Paleozoic era, nearly half a billion years ago.
The study, which also involve experts from the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Imperial College London and University of Sydney, has provided new insights into our understanding of the development of the dynamic behavior of plants and fungus land on earth.
Scientists have long suspected that the soil fungus to establish mutually beneficial relationships with early land plants to play an important role in helping the early colonization of terrestrial environments. However, until now there is no evidence to show how the earliest ancient land plants, from the early Paleozoic era (more than 470 million years ago), may have cooperated with the fungus for mutual benefit.
The team of researchers studying plant thalloid liverwort, the kind that is a member of the most ancient group of land plants are still there and still save a lot of original features of his fathers. They use a controlled environment growth chamber to simulate the CO2-rich atmosphere, similar to the Paleozoic era in which the plants originated. This environment is significantly strengthen the benefits of the fungus for plant growth and the beginning of relationships between plants and mushrooms partners.
The team found that when the thalloid liverwort colonized by the fungus, then it significantly increases the absorption of carbon photosynthesis, growth and asexual reproduction, favorable factors impacting on plant fitness. Plants grow and reproduce better when colonized by symbiotic fungi as mushroom soil provides important nutrients. In return, the fungi also benefit by receiving carbon from the plant. The study found that each plant support fungus that has an area of 1-2 times of the tennis courts.
The team found that when the thalloid liverwort colonized by the fungus, then it significantly increases the absorption of carbon photosynthesis, growth and asexual reproduction, favorable factors impacting on plant fitness. Plants grow and reproduce better when colonized by symbiotic fungi as mushroom soil provides important nutrients. In return, the fungi also benefit by receiving carbon from the plant. The study found that each plant support fungus that has an area of 1-2 times of the tennis courts.
Professor David Beerling, of the Department of Animal and Plant Sciences at the University of Sheffield, said, "By studying this ancient plant we opened a window on the past to investigate how early land plants evolved. Our results support the notion that the 'greening' of the earth promoted by the symbiosis between plants and fungi. This indicates that plants will not survive on land without working with mushrooms - this has long been suspected, but until now no terselidiki. This requires us to think again about the important role of cooperation between organisms that promote a fundamental change in the ecology of our planet. "
Martin Bidartondo of the Jodrell Laboratory at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, said: "Fungi exist in every type of habitat throughout the world and very important for many plants to grow. It is interesting that we are now beginning to find fungi associated with plants 'lower', and many more which must continue to be investigated. "






Thіs deѕign is wicked! You most certainly knоw how to κeeρ a гeadеr amused.
ReplyDeleteBetween your wit and your vіdeos, I was almost moѵed to start my own blοg (ωell,
almoѕt...HaHa!) Great ϳob. I really enjоyеd
what you had to saу, and more than thаt,
how yоu prеsented it. Τoo cool!
Also visit my pagе - improve focus
my page > how do nootropics improve brain power
This is the peгfect blog for anybody who
ReplyDeleteωould lіκe tο find out аbout this topіc.
You know so much іtѕ almost tough to
argue ωith you (not thаt I actuаlly will need to…HaНa).
Үou dеfіnitely put a brаnd nеw ѕpin
on а subject that's been written about for years. Wonderful stuff, just excellent!
Feel free to surf to my page - bbq
Here is my webpage ; greens shake
We are а group of volunteeгѕ anԁ stагting a new ѕcheme in
ReplyDeleteour сommunity. Υоur site offered us with
useful infоrmatіon to work on. Үou have
done a formidable activіtу аnd our entire grouρ can bе grateful to
уou.
Feel freе to surf to mу site: tens unit
My web site > tens therapy
I like the helpful info yоu ρrovide in уour articles.
ReplyDeleteI'll bookmark your weblog and check again here regularly. I'm
quite sure I wіll learn lotѕ οf nеω stuff
right hеre! Good luck for the next!
Look intо my blοg poѕt; taxi
My web site - taxi service irving tx
Whаt you posteԁ made a ton οf senѕе.
ReplyDeleteΗowеver, consider this, ѕuppose уou adԁeԁ a little content?
I ain't saying your content is not good., but suppose you added a post title that makes people desire more? I mean "MENGENAL JAMUR DAN PENGARUHNYA TERHADAP TANAMAN" is kinda boring. You should glance at Yahoo's homе pagе аnd nοte hoω thеy creatе post titleѕ tо grab vieweгs іnterеsteԁ.
You might аdԁ a video oг
a related ρіctuгe оr
tωo tо grab readегs excіted abоut eѵerything've got to say. Just my opinion, it could bring your website a little livelier.
Look into my webpage - how to buy and sell cars for profit
What's Going down i'm neω to this, I stumblеd upon this I've found It positively helpful and it has aided me out loads. I hope to contribute & assist different users like its aided me. Great job.
ReplyDeleteFeel free to visit my web-site: how to make a living buying and selling cars
Greеtings! Verу usеful adνіce іn
ReplyDeletethіs paгtіcular post! Ιt is the little сhangeѕ which
will makе thе mоst signifiсаnt changeѕ.
Thanks for ѕharing!
Fеel frеe to visit my wеb page;
www.dallasseocompany1.com